
The Earth is constantly recycling elements and materials that make up the Earth’s crust and mantle. This process is known as the Earth’s recycling process, and it is responsible for the recycling of materials inside the ocean crust and the formation of new rocks and minerals.
In this article, we will take an in-depth look into the recycling processes that take place, how the different types of rocks are related, and how this process affects life on Earth. To answer the question what is the name for the process of recycling materials that make up the earth’s crust and mantle?
How Does the Earth Recycle Elements?
The Earth’s recycling process involves the movement of materials from the crust and upper mantle to the deeper mantle. This process is part of the rock cycle, which is a continuous process in which materials are recycled and transformed from one type to another. The processes that are involved in this recycling process include subduction, melting, metamorphism, and lithification.
Subduction is a process in which the oceanic plates slide beneath the continental plates. As the oceanic plate moves downwards, it carries with it the sediment and rocks that have been deposited on its surface. The sediment and rocks become part of the mantle as they are subducted and recycled.
Melting is the process in which rocks melt due to the extreme heat and pressure that is present in the deep mantle. As the rocks melt, magma is formed and travels upwards toward the Earth’s surface. This magma can then erupt from volcanoes and form new rocks and minerals, which are then recycled into the Earth’s crust.
Metamorphism is the process in which rocks are changed from one type to another due to the heat and pressure that is present on the Earth’s surface. This process can take place when rock is exposed to extreme temperatures and pressure, and is often caused by tectonic activity. This process can also be triggered by the collision of two plates, which can cause intense heat and pressure.
Lithification is the process in which sediment and rocks are compressed by the pressure and heat of the Earth’s mantle. This process can lead to the formation of sedimentary and metamorphic rocks.
What is the name for the process of recycling materials that make up the Earth’s crust and mantle?
The name for the process of recycling materials that make up the Earth’s crust and mantle is the Earth’s recycling process. The role of water and other volatiles in the melting of existing crustal rock in the wedge above a subduction zone is the most important part of the cycle.
Volcanic eruptions have an important role to play in the formation of the overlying rock that we find in many parts of the world. When molten material and gas are trapped inside the outer part of the volcano, they form new minerals that eventually become part of the rock that we see today.
This process starts with a molten material known as buoyant magma, which is the hotter material from the depths of the Earth. As the molten material rises to the surface, the surrounding pressure decreases, causing the minerals to form a crystalline structure. The gas trapped inside the magma also plays an important role in the formation of the rock as it expands when it is heated.
As the magma nears the surface, it cools and solidifies, forming the overlying rock. The gas that was trapped inside the magma is released, and the minerals from the magma are deposited on the surface. The minerals can also react with the ion-rich atmosphere, forming new minerals and eventually becoming part of the rock.
What is the process that recycles old crust?
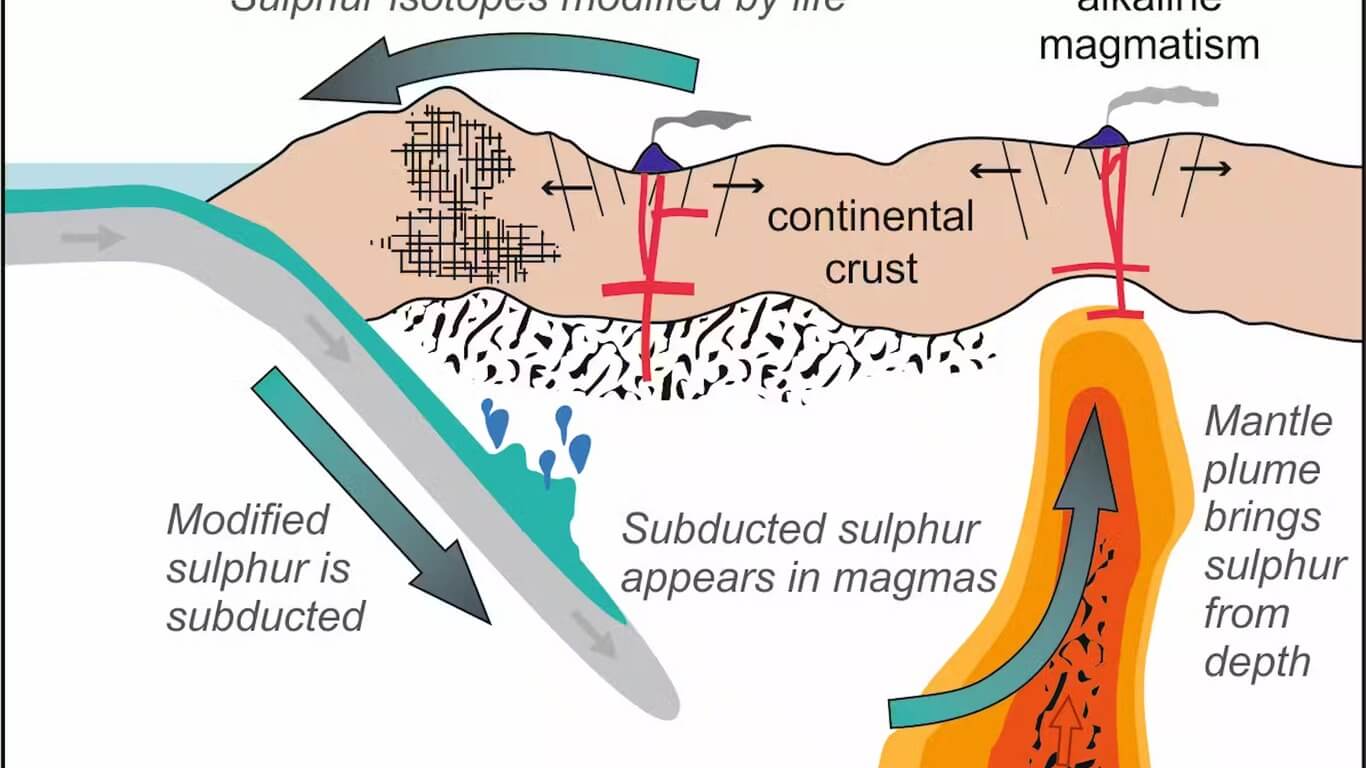
The process that recycles old crust is subduction, which is the process by which the oceanic plates slide beneath the continental plates. As the oceanic plate moves downwards, it carries with it the sediment and rocks that have been deposited on its surface. The sediment and rocks become part of the mantle as they are subducted and recycled.
Geology is the scientific study of the Earth, its materials, structure, processes, and history. It is a vast science covering the physical structure of the planet and how it acts, interacts and changes over time. Weather, mantle and crust, pieces of rock, and denser minerals are all studied in geology. The Earth’s crust is made up of many different rock types, each one related to the other in some way. Pieces of rock that are denser and heavier than the rest are generally found deep within the crust. Over time, these pieces of rock are transferred and moved around due to a variety of natural causes.
One of the most important forces involved in this transfer is the process of subduction. This occurs when two pieces of the Earth’s crust are pushed together due to the temperature and pressure of the mantle. As the pieces of crust are pushed together, they become denser and heavier, moving further down into the Earth’s mantle. Subduction is important to the study of geology because it helps explain why certain rock types are related to each other.
What is the name of the processes that recycle material inside the ocean crust?
The process that recycles material inside the ocean crust is called melting. This is the process in which rocks melt due to the extreme heat and pressure that are present in the deep mantle. As the rocks melt, magma is formed and travels upwards toward the Earths surface. This magma can then erupt from volcanoes and form new rocks and minerals, which are then recycled into the Earth’s crust. Read when the garbage chute was invented.
Where is the crust being recycled into the mantle?
The crust is recycled into the mantle through subduction, which is the process by which the oceanic plates slide beneath the continental plates. As the oceanic plate moves downwards, it carries with it the sediment and rocks that have been deposited on its surface. The sediment and rocks become part of the mantle as they are subducted and recycled. These plates include both oceanic and continental crusts, which are formed from volcanic eruptions and sedimentary rocks.
The process of plate tectonics involves the gradual movement of these plates. At times, one plate will be forced underneath another, forming a subduction zone. During subduction, the denser oceanic plate is pushed below the continental plate, creating a deep trench in the seafloor. As the plate moves downwards, the rocks of the plate are subjected to extreme temperatures and pressures. This causes the plate to be fragmented into a slab, which is then subducted below the continental plate.
What is Earth’s crust made up of?
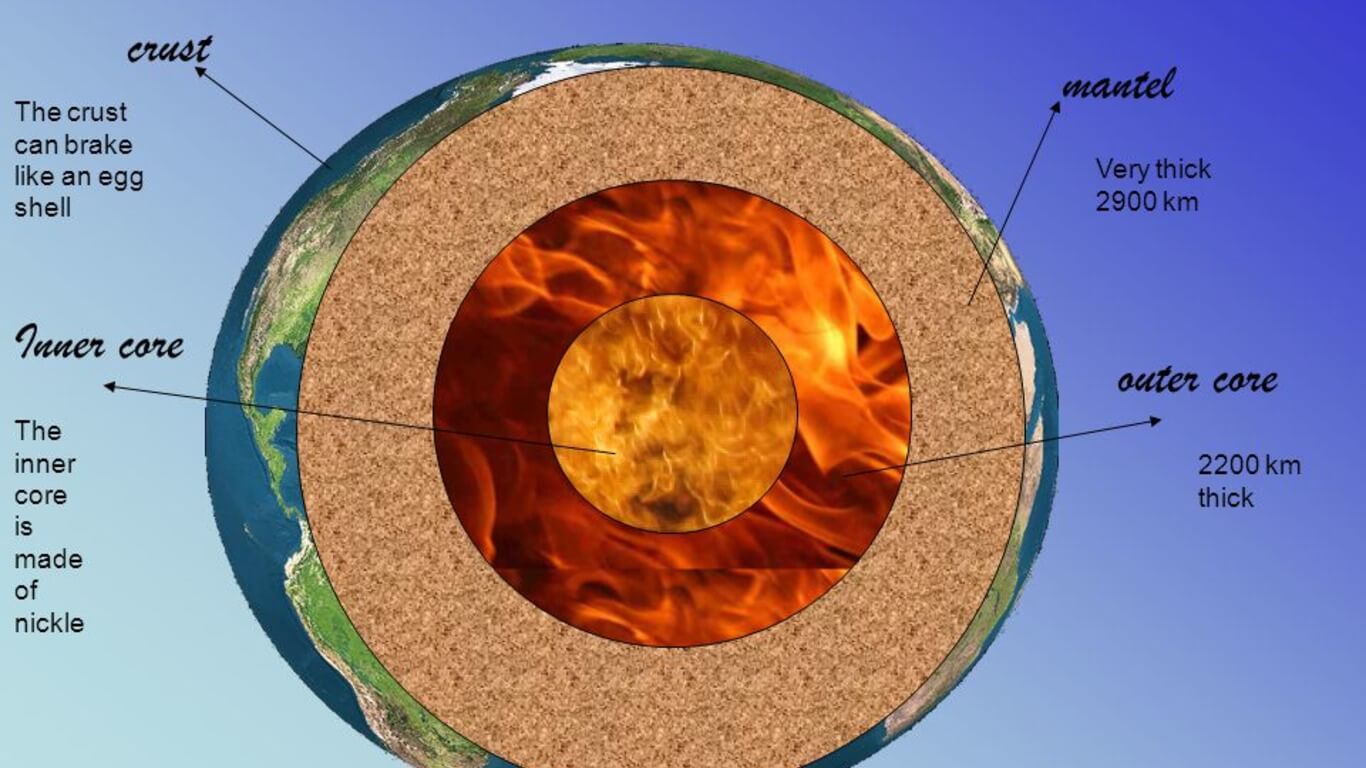
Earth’s crust is made up of two main types of rock: sedimentary and igneous. Sedimentary rocks are formed from the deposition of sediment, such as sand, clay, and silt. Igneous rocks are formed when magma cools and solidifies. Rocks are the most visible part of the Earth, and geologists use them to study various aspects of the Earth. Geologists also study how rock changes over time.
The Earths surface is composed of tectonic plates that move and interact with each other. These plates are made up of two different types of crust: oceanic and continental. Oceanic crust is denser and thinner than continental crust and is made mostly of igneous rocks formed from cooling magma.
The continental crust is thicker and less dense than the oceanic crust and is made up of sedimentary rock. An earthquake can also occur when two plates collide, as the Earth’s crust is deformed and releases energy in the form of seismic waves.
How are materials recycled by convection currents?
Materials are recycled through convection currents within the mantle. Convection currents are created when hot, less-dense material rises, and cold, more-dense material sinks. As the material rises and falls, it transports materials and heat throughout the mantle. This process is also responsible for the formation of tectonic plates and other geological features.
Rocks are the most visible part of the Earth, and geologists use them to study various aspects of the Earth. Erosion is the process of material being moved from one place to another. Both processes are important in the formation of new rock, and the erosion of landforms. Rocks on the surface of the Earth can be changed by events such as lava flows, earthquakes, and landslides.
The mantle is the layer beneath the crust and is composed of a hot, semi-solid rock called the asthenosphere. This layer is a kilometer thick and is home to many of the Earth’s active geologic processes. The movement of these plates can cause earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, and other seismic events. Geology is a fascinating field of science that has been studied for millions of years.
What is the meaning of lithosphere?
The biosphere includes a part of the earth that supports life. The lithosphere includes non-living matter. The lithosphere is the outermost layer of the Earths surface and is divided into pieces called tectonic plates. The lithosphere is a brittle layer and is made up of solid rock. This layer is responsible for the movement of tectonic plates, which is responsible for earthquakes and other geological events.
An electronic deposit, or an ion deposit, is when you transfer money electronically using a bank app or online banking. Another part of the deposit is convenient, fast and secure as it allows you to transfer money without having to physically visit a bank branch.
The lithosphere is divided into two main sections: continental and oceanic. The continental lithosphere is characterized by thicker, older rocks and a low concentration of minerals.
How does the rock cycle recycle materials?
The rock cycle is the process in which rocks are recycled through processes such as subduction, melting, metamorphism, and lithification.
The oceanic crust is usually composed of basalt, which is a dark-colored, fine-grained igneous rock, and kimberlites, which are a type of igneous rock that is rare and often associated with diamond deposits.
When the pressure and temperature of the Earth’s lithosphere move apart, due to tectonic plate movement, high temperatures and pressures are created in the mantle and the crust. This creates molten rock, which is known as magma. Magma rises to the Earths surface and creates volcanic eruptions.
The minerals and elements that form Earth’s equilibrium are essential for life on Earth. Without them, the Earth would not be able to support life and its climate would drastically change. Therefore, it is very important to understand mineralogy, the composition of seawater, and the movement of tectonic plates to maintain Earth’s equilibrium.
What is the biogeo cycle?
So, what is the biogeo cycle? This is the term used to describe the cycle of biological, geological, and chemical processes that take place on Earth. This cycle includes the rock cycle and the gaseous cycle.
What is meant by a rock cycle?
The rock cycle is the process in which rocks are formed, changed, and recycled. Rocks are formed when molten material cools and solidifies. They can then be changed by weathering and erosion. This process recycles the crust and is how Earth’s crust is recycled.
What is a gaseous cycle?
The gaseous cycle is the process in which gases are exchanged between Earth’s atmosphere and its surface. This includes the exchange of water vapor, carbon dioxide, and other gases. This cycle is responsible for Earth’s climate and weather.
What is the bottom of the sea called?
The bottom of the sea is called the seafloor. This is where sediment accumulates and is recycled through the rock cycle.
What’s the lithosphere divided into pieces called?
The lithosphere is the solid part of Earths surface and is divided into pieces called plates. These plates move around on the surface and interact with each other in a process known as plate tectonics.
Plate tectonics
Plate tectonics is a process in which plates move around and interact with each other. These interactions include spreading ridges, subduction zones, and continental collisions. These are all processes that recycle Earth’s crust.
Accelerated erosion
Accelerated erosion is a process in which weather and water wear away the land surface more quickly than usual. This process increases the rate at which Earth’s crust is recycled.
An evolving process
The biogeo cycle is an evolving process and one that is constantly changing.
Spreading ridges
Spreading ridges are the opposite of subduction zones – they are areas where the tectonic plates that make up the Earth’s crust are being pulled apart. As the plates pull apart, they form a ridge that often creates an oceanic trench. This trench is often filled with magma, and as it cools and solidifies, a new oceanic crust is formed. Over time, this new crust spreads out and creates new seafloor.
Subduction zones
Subduction zones form when one plate, usually an oceanic plate, is pushed underneath another plate. This often happens at oceanic trenches, because the oceanic plate is much denser than the continental plate and is pulled down beneath it. Subduction zones create volcanoes because the magma is heated and released at the surface.
Continental collision
Continental collisions occur when two continental plates meet and push up against each other. This creates a mountainous region, as the two plates push up against each other and form a mountain range. The Himalayas and the Rockies are examples of continental collisions.
What Process Recycles the Crust?
The process that recycles the Earth’s crust is called plate tectonics. This process involves the movement of large plates of the Earth’s lithosphere, which is the solid outer layer of the Earth. These plates move and interact in various ways, such as spreading ridges, subduction zones, and continental collisions. Plate tectonics also contributes to accelerated erosion and an evolving process of the Earth’s crust.
The role of water
Water plays an important role in the biogeo cycle, as it is involved in all of the processes mentioned above.
What Process Recycles the Crust?
The process that recycles the Earth’s crust is called plate tectonics. This process involves the movement of large plates of the Earth’s lithosphere, which is the solid outer layer of the Earth. These plates move and interact in various ways, such as spreading ridges, subduction zones, and continental collisions. Plate tectonics also contributes to accelerated erosion and an evolving process of the Earth’s crust.
How is Earth’s Crust Recycled Quizizz?
Earth’s crust is recycled through plate tectonics. Plate tectonics is the movement and interaction of the Earth’s lithosphere, which is the solid outer layer of the Earth.
The movement of the tectonic plates causes different processes, such as spreading ridges, subduction zones, and continental collisions. These processes cause the Earth’s crust to be recycled, which is an essential part of the rock cycle and the Earth’s natural processes.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the bio geo cycle, rock cycle, and gaseous cycle are all important processes involved in the recycling of Earth’s crust. Plate tectonics, spreading ridges, subduction zones, continental collision, accelerated erosion, and the role of water all play a part in this process, which is constantly evolving.
